Will Engineer Advanced 3D Printed Parts For NASA's Orion Mission
Stratasys Ltd. and Phoenix Analysis & Design Technologies are teaming with Lockheed Martin Space to deliver next-generation 3D printed parts for NASA’s Orion deep-space spacecraft. Key to the project are Stratasys advanced materials – including an ESD variant of the new Antero 800NA, a PEKK-based thermoplastic offering high performance mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties.
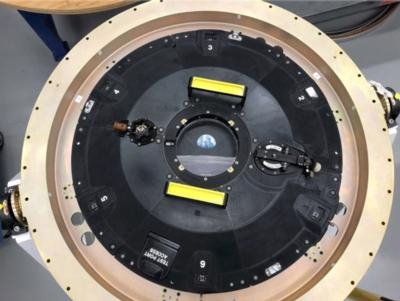
Orion is NASA’s spacecraft that will send astronauts to the Moon and beyond. Orion’s next test flight, dubbed Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), will be the first integration mission with the world’s most powerful rocket, the Space Launch System, where an un-crewed Orion will fly thousands of miles beyond the Moon during an approximately three week mission.
The following flight, EM-2, will also go near the Moon, but with astronauts on board, a first since 1972 and will enable NASA to prepare for increasingly complex missions in deep space. The mission will use more than 100 3D printed production parts on board, engineered in conjunction with Lockheed Martin, Stratasys and PADT.
The production-grade, thermoplastic 3D printed parts for NASA’s Orion vehicle are produced at the Additive Manufacturing Lab at Lockheed Martin in conjunction with PADT, which now employs the latest in Stratasys 3D printers and materials. Using advanced materials such as ULTEM 9085 resin and the new Antero material incorporating critical electro-static dissipative (ESD) functionality – NASA could meet key requirements for 3D printed parts to perform in the extremes of deep space. Antero is ideally suited to meet NASA’s requirements for heat and chemical resistance, along with the ability to withstand high mechanical loads.
“Working with PADT, Stratasys, and NASA has enabled us to achieve highly consistent builds that move beyond the realm of prototyping and into production,” said Brian Kaplun, Manager of Additive Manufacturing at Lockheed Martin Space. “We’re not just creating parts, we’re reshaping our production strategy to make spacecraft more affordable and faster to produce.”

The Lockheed Martin, Stratasys and PADT-engineered collaboration is differentiated by an ability to create consistency and repeatability in mass scale across the entire additive manufacturing part production process. Lockheed Martin is also one of the first customers leveraging Stratasys’ Antero, using the new thermoplastic for a critical part situated just outside of Orion’s docking hatch. The complex part consists of six individual 3D printed components locked together to form a ring on the craft’s exterior. The part is currently on display in the Lockheed Martin booth #603 at the 34th Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, CO April 16-19.
“The demands of space travel require extremely high performance materials and the most rigorous manufacturing processes in the industry. Part integrity and repeatability are essential and must pass NASA’s demanding testing and validation process,” said Scott Sevcik, Vice President of Manufacturing at Stratasys. “Based on decades of experience delivering strong and lightweight additive manufacturing solutions for leaders across the aerospace industry, Stratasys technology is ideally suited to match the high-reliability manufacturing processes required for production parts in space exploration.”
“It’s exciting to be a part of the Orion mission and Lockheed Martin’s efforts to transition additive manufacturing from prototyping to production,” said Rey Chu, Principal and Co-Owner at PADT. “Additive manufacturing technology and materials have come a long way to become a full-fledged end-use manufacturing option.”
(Image provided with Stratasys news release and from file)
 ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.01.24): Say Altitude
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.01.24): Say Altitude ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.01.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.01.24) Classic Aero-TV: Korean War Hero Twice Reborn
Classic Aero-TV: Korean War Hero Twice Reborn Airborne 04.29.24: EAA B-25 Rides, Textron 2024, G700 Deliveries
Airborne 04.29.24: EAA B-25 Rides, Textron 2024, G700 Deliveries Airborne Affordable Flyers 05.02.24: Bobby Bailey, SPRG Report Cards, Skydive!
Airborne Affordable Flyers 05.02.24: Bobby Bailey, SPRG Report Cards, Skydive!




