Wed, Aug 13, 2014
Advertisement
More News
 Airborne-Flight Training 05.09.24: ERAU at AIAA, LIFT Diamond Buy, Epic A&P
Airborne-Flight Training 05.09.24: ERAU at AIAA, LIFT Diamond Buy, Epic A&P
Also: Vertical Flight Society, NBAA Maintenance Conference, GA Honored, AMT Scholarship For the first time, students from Embry-Riddle’s Daytona Beach, Florida, campus took t>[...]
 ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.07.24): Hazardous Weather Information
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.07.24): Hazardous Weather Information
Hazardous Weather Information Summary of significant meteorological information (SIGMET/WS), convective significant meteorological information (convective SIGMET/WST), urgent pilot>[...]
 Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.07.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.07.24)
"The need for innovation at speed and scale is greater than ever. The X-62A VISTA is a crucial platform in our efforts to develop, test and integrate AI, as well as to establish AI>[...]
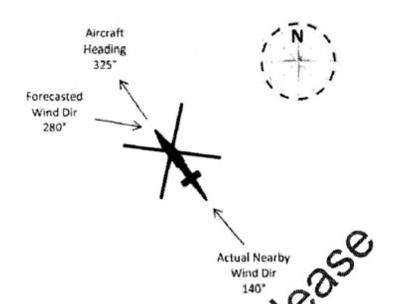
 NTSB Final Report: Cessna 150
NTSB Final Report: Cessna 150
(FAA) Inspector Observed That Both Fuel Tanks Were Intact And That Only A Minimal Amount Of Fuel Remained In Each Analysis: According to the pilot, approximately 8 miles from the d>[...]
 Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.08.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.08.24)
“Pyka’s Pelican Cargo is unlike any other UAS solution on the market for contested logistics. We assessed a number of leading capabilities and concluded that the Pelica>[...]
blog comments powered by Disqus