Aircraft Flew More Than 100 Nautical Miles Along The Coast Through Controlled Airspace
A recent experimental flight proves that unmanned aircrafts can be used not only for short round trips, but also for long distance operations from airfield to airfield. This opens up new possibilities for long-range drone applications such as surveillance, monitoring, search and rescue operations and applications within transportation.

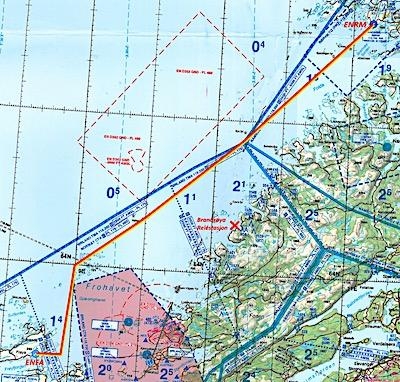
In the morning of June 5th, a Maritime Robotics integrated PenguinB UAV owned by the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (FFI), took off from Frøya on the mid-western coast of Norway. After launch by a 2-person crew from Maritime Robotics, the small unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) flew north towards the sea, beginning its first long haul mission. As it flew on its 108 nautical mile route high above the rough Norwegian terrain, it was always connected to the operations center by novel long-range communication technology. The plane flew steadily through the sky on its carefully planned and monitored voyage, through different types of controlled civil airspace handled by civil air traffic control.
When the aircraft approached Rørvik, the landing operator took over control and landed the aircraft smoothly. The Norwegian University of Technology and Science (NTNU) was a part of the landing crew, where they provided their mobile operations station and safety pilot to assist with the final approach and landing. Upon landing, the small UAV had been in the air for 2 hours and 12 minutes. Flying a route of 200 kilometers and landing approximately 170 kilometers from where it took off.
Innovative new wireless data link technology using phased array antennas from Radionor Communications provided reliable communication for control during the mission, and stable communication to the ground network with range above 86 nautical miles was recorded with a lightweight transceiver installed in the aircraft.
This mission served to prove that it is possible to operate an unmanned aircraft not only on round trips from one base, but for operations involving transit between multiple bases. This is a game changer for designing flexible UAV missions and services. One example is monitoring/surveillance missions (or search and rescue missions). During these missions, the main operations area might drift or move into an area far away from where the aircraft took off. This new area could be closer to an alternative landing site, if the aircraft can land at this alternative site then it is able to stay in the air for a longer duration. Another example is freight, where it has very little effect to use UAS if the transport vehicle isn’t able to land at a different base from where it began.
Planning the mission involved Avinor, the company providing air traffic management for Norwegian airspace. It was clear that in order for the flight to be successful, a degree of flexibility was needed. The ability to fly in controlled airspace was a game changer for the mission and fitting the UAV with a transponder (normally used for manned aircrafts) was key to giving those responsible for airspace safety confidence in the flight plan. In order to effectively maintain command and control capabilities for the entire flight, the status and telemetry from the unmanned aircraft had to be accessible online. In this operations all control was made from Rørvik or Frøya , but in principle the flight could have been controlled from specialized crew in a control room anywhere with good network access.
The experiment was a part of the research program Hybrid Operations in the Maritime Environment (HOME), which is a cooperation between Radionor Communications, Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Maritime Robotics. This project has been partly funded by the Norwegian Research Council. In addition, the experiment was made possible due to important contribution from the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (FFI), Norkringand Avinor.
(Images provided with Maritime Robotics news release)
 ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.25.24): Airport Rotating Beacon
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.25.24): Airport Rotating Beacon ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.25.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.25.24) Klyde Morris (04.22.24)
Klyde Morris (04.22.24) Airborne 04.24.24: INTEGRAL E, Elixir USA, M700 RVSM
Airborne 04.24.24: INTEGRAL E, Elixir USA, M700 RVSM Airborne 04.22.24: Rotor X Worsens, Airport Fees 4 FNB?, USMC Drone Pilot
Airborne 04.22.24: Rotor X Worsens, Airport Fees 4 FNB?, USMC Drone Pilot




