Sun, Feb 23, 2014
'Hot Flow Anomalies' Can Occur Multiple Times Each Day
Researchers recently discovered that a common space weather phenomenon on the outskirts of Earth’s magnetic bubble, the magnetosphere, has much larger repercussions for Venus. The giant explosions, called hot flow anomalies, can be so large at Venus that they’re bigger than the entire planet and they can happen multiple times a day.
"Not only are they gigantic," said Glyn Collinson, a space scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. "But as Venus doesn’t have a magnetic field to protect itself, the hot flow anomalies happen right on top of the planet. They could swallow the planet whole."
Collinson is the first author of a paper on these results that appeared online in the Journal of Geophysical Research in February 2014. The work is based on observations from the European Space Agency's Venus Express. The results show just how large and how frequent this kind of space weather is at Venus.
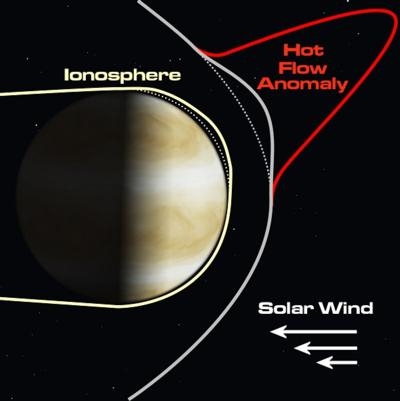
Earth is protected from the constant streaming solar wind of radiation by its magnetosphere. Venus, however, has no such luck. A barren, inhospitable planet, with an atmosphere so dense that spacecraft landing there are crushed within hours, Venus has no magnetic protection.
Scientists like to compare the two: What happened differently at Earth to make it into the life-supporting planet it is today? What would Earth be like without its magnetic field? At Earth, hot flow anomalies do not make it inside the magnetosphere, but they release so much energy just outside that the solar wind is deflected, and can be forced to move back toward the sun. Without a magnetosphere, what happens at Venus is very different.
Venus's only protection from the solar wind is the charged outer layer of its atmosphere called the ionosphere. A sensitive pressure balance exists between the ionosphere and the solar wind, a balance easily disrupted by the giant energy rush of a hot flow anomaly. The hot flow anomalies may create dramatic, planet-scale disruptions, possibly sucking the ionosphere up and away from the surface of the planet.
(Image provided by NASA)
More News
From 2023 (YouTube Version): Legacy of a Titan Robert (Bob) Anderson Hoover was a fighter pilot, test pilot, flight instructor, and air show superstar. More so, Bob Hoover was an i>[...]
Get The Latest in Aviation News NOW on Instagram Are you on Instagram yet? It's been around for a few years, quietly picking up traction mostly thanks to everybody's new obsession >[...]
Aero Linx: B-52H Stratofortress The B-52H Stratofortress is a long-range, heavy bomber that can perform a variety of missions. The bomber is capable of flying at high subsonic spee>[...]
Altimeter Setting The barometric pressure reading used to adjust a pressure altimeter for variations in existing atmospheric pressure or to the standard altimeter setting (29.92).>[...]
"Knowing that we play an active part in bettering people's lives is extremely rewarding. My team and I are very thankful for the opportunity to be here and to help in any way we ca>[...]
 Classic Aero-TV: Remembering Bob Hoover
Classic Aero-TV: Remembering Bob Hoover ANN FAQ: Follow Us On Instagram!
ANN FAQ: Follow Us On Instagram! ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.15.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.15.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.15.24):Altimeter Setting
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.15.24):Altimeter Setting Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.16.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.16.24)



