Sat, Apr 12, 2003
Covering Twice The Ground
 If NASA has its way, not one, but two rovers will
soon be roaming the Red Planet, investigating areas that might have
once held bodies of water.
If NASA has its way, not one, but two rovers will
soon be roaming the Red Planet, investigating areas that might have
once held bodies of water.
NASA managers announced the two landing sites for the Mars
Exploration Rovers (MERs) Friday, saying both sites were
scientifically compelling. Four prospects were under consideration
and NASA made its final decision based not only on scientific
allure, but spacecraft technical concerns, said space science
program chief Ed Weiler.
"In choosing where to go, we need to balance science value with
engineering safety considerations," said Weiler. The first rover,
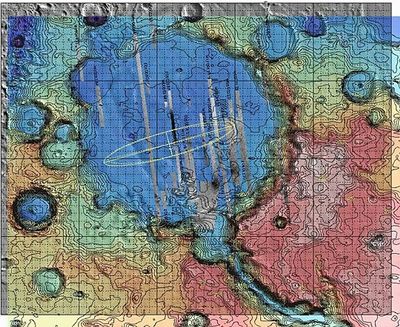
scheduled for launch on May 30, will be directed to Gusev Crater,
located 15 degrees south of Mars' equator (see map, bottom). The
second robotic scout, slated for liftoff on June 25, is targeted to
land at Meridiani Planum, which features rich deposits of gray
hematite, an iron oxide mineral associated with water. Meridiani
Planum is about 2 degrees south of the equator and halfway around
the planet from Gusev Crater.

Doing The Job Before The Lights Go Out
The first rover should reach its landing site on Jan. 4 and the
second on Jan. 25. Each is expected to last for about three months
before dust blankets the rovers' solar arrays, cutting off their
power. The rovers' masts will carry remote sensing instruments,
including high-resolution color cameras and infrared spectrometers
for studying the minerals in rocks and soil. The rovers also will
be equipped with a microscopic imager to see micron-size particles
and textures, an alpha-particle/x-ray spectrometer to determine
what elements the samples contain, and a Moessbauer spectrometer
for determining the mineralogy of iron-bearing rocks.
Each rover will carry a rock abrasion tool, similar to a
geologist's rock hammer, to remove weathered surfaces from rocks
and expose their interiors for analysis. The overall scientific
focus of the mission is to investigate what role water played on
Mars and to determine how suitable the conditions would have been
for life, said Cornell University's Steve Squyres, a principal
investigator.
More News
Aero Linx: Model Aeronautical Association of Australia MAAA clubs are about fun flying, camaraderie and community. For over 75 years, the MAAA has been Australia’s largest fl>[...]
Touchdown Zone Lighting Two rows of transverse light bars located symmetrically about the runway centerline normally at 100 foot intervals. The basic system extends 3,000 feet alon>[...]
“Discovery and innovation are central to our mission at Virgin Galactic. We’re excited to build on our successful record of facilitating scientific experiments in subor>[...]
How To Get A Story On Aero-TV News/Feature Programming How do I submit a story idea or lead to Aero-TV? If you would like to submit a story idea or lead, please contact Jim Campbel>[...]
Student Pilot Reported That During Rotation, “All Of A Sudden The Back Of The Plane Kicked To The Right..." Analysis: The student pilot reported that during rotation, “>[...]
 ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.02.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.02.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.02.24): Touchdown Zone Lighting
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.02.24): Touchdown Zone Lighting Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.02.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.02.24) ANN FAQ: Contributing To Aero-TV
ANN FAQ: Contributing To Aero-TV NTSB Final Report: Cirrus Design Corp SR20
NTSB Final Report: Cirrus Design Corp SR20





