Mars Exploration Rover Mission Status Update
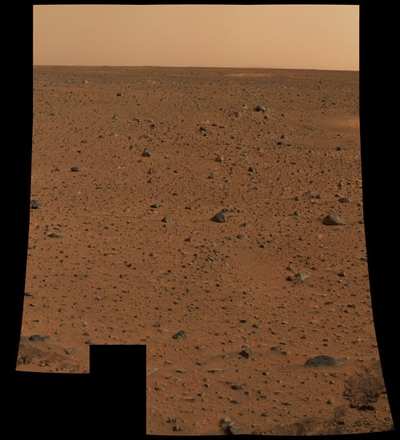
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit drove on Thursday for the
first time since April 8, acting on commands from engineers who are
still investigating bouts of amnesia and other unusual behavior
exhibited by Spirit in the past two weeks. The drive took Spirit
about 5.6 feet toward destinations about about 500 feet away.
The rover has already operated more than 20 times longer than its
original prime mission on Mars.

This week, rover engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory,
Pasadena, Calif., judged that it would be safe to send Spirit
commands for Thursday's drive. They also anticipated that, if the
rover did have another amnesia event, the day's outcome could be
helpful in diagnosing those events.
Three times in the past two weeks, Spirit has failed to record
data from a day's activity period into non-volatile flash memory.
That is a type of computer memory where information is preserved
even when power is off, such as when the rover naps to conserve
power.
"We expect we will see more of the amnesia events, and we want
to learn more about them when we do," said JPL's Sharon Laubach,
chief of the rover sequencing team, which develops and checks each
day's set of commands.
 The team is also investigating two
other types of problems Spirit has experienced recently: failing to
wake up for three consecutive communication sessions about two
weeks ago and rebooting its computer on April 11, 12 and 18.
Engineers have not found any causal links among these three types
of events. After checking last week whether moving the rover's
high-gain antenna could trigger problems, routine communication via
that dish antenna resumed Monday.
The team is also investigating two
other types of problems Spirit has experienced recently: failing to
wake up for three consecutive communication sessions about two
weeks ago and rebooting its computer on April 11, 12 and 18.
Engineers have not found any causal links among these three types
of events. After checking last week whether moving the rover's
high-gain antenna could trigger problems, routine communication via
that dish antenna resumed Monday.
Spirit has maintained stable power and thermal conditions
throughout the problem events this month, although power output by
its solar panels has been significantly reduced since mid-2007 by
dust covering the panels.
"We decided not to wait until finishing the investigations
before trying to drive again," Laubach said. "Given Spirit's
limited power and the desire to make progress toward destinations
to the south, there would be risks associated with not
driving."

The team has made a change in Spirit's daily routine in order to
aid the diagnostic work if the rover experiences another failure to
record data into flash memory.
To conserve energy, Spirit's daily schedule since 2004 has
typically included a nap between the rover's main activities for
the day and the day's main downlink transmission of data to Earth.
Data stored only in the rover's random-access memory (RAM), instead
of in flash memory, is lost during the nap, so when Spirit has a
flash amnesia event on that schedule, the team gets no data from
the activity period. The new schedule puts the nap before the
activity period. This way, even if there is a flash amnesia event,
data from the activity period would likely be available from RAM
during the downlink.

Spirit and its twin, Opportunity, completed their original
three-month prime missions on Mars in April 2004 and have continued
their scientific investigations on opposite sides of the planet
through multiple mission extensions. Engineers have found ways to
cope with various symptoms of aging on both rovers.
This week, Opportunity completed drives of 96 315 feet Tuesday,
449 feet Wednesday and 312 feet Thursday in its long-term trek
toward a crater more than 20 times larger than the biggest it has
visited so far. JPL, a division of the California Institute of
Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Exploration Rover project
for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
 Unfortunate... ANN/SportPlane Resource Guide Adds To Cautionary Advisories
Unfortunate... ANN/SportPlane Resource Guide Adds To Cautionary Advisories ANN FAQ: Turn On Post Notifications
ANN FAQ: Turn On Post Notifications ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.29.24): Visual Approach Slope Indicator (VASI)
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.29.24): Visual Approach Slope Indicator (VASI) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.28.24): Airport Marking Aids
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.28.24): Airport Marking Aids ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.28.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.28.24)







