Helps Astronomers Understand Chemical Processes During Planetary Formation
The organic molecule methyl alcohol (methanol) has been found by the Atacama Large Millimeter/Submillimeter Array (ALMA) in the TW Hydrae protoplanetary disc. This is the first such detection of the compound in a young planet-forming disc. Methanol is the only complex organic molecule as yet detected in discs that unambiguously derives from an icy form. Its detection helps astronomers understand the chemical processes that occur during the formation of planetary systems and that ultimately lead to the creation of the ingredients for life.
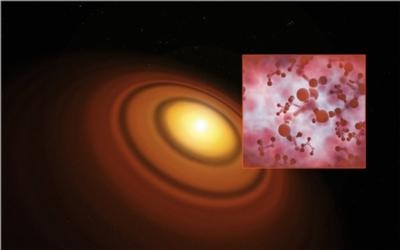
The protoplanetary disc around the young star TW Hydrae is the closest known example to Earth, at a distance of only about 170 light-years. As such it is an ideal target for astronomers to study discs. This system closely resembles what astronomers think the Solar System looked like during its formation more than four billion years ago.
The Atacama Large Millimeter/Submillimeter Array (ALMA) is the most powerful observatory in existence for mapping the chemical composition and the distribution of cold gas in nearby discs. These unique capabilities have now been exploited by a group of astronomers led by Catherine Walsh (Leiden Observatory, the Netherlands) to investigate the chemistry of the TW Hydrae protoplanetary disc.
The ALMA observations have revealed the fingerprint of gaseous methyl alcohol, or methanol (CH3OH), in a protoplanetary disc for the first time. Methanol, a derivative of methane, is one of the largest complex organic molecules detected in discs to date. Identifying its presence in pre-planetary objects represents a milestone for understanding how organic molecules are incorporated into nascent planets.
Furthermore, methanol is itself a building block for more complex species of fundamental prebiotic importance, like amino acid compounds. As a result, methanol plays a vital role in the creation of the rich organic chemistry needed for life.
Catherine Walsh, lead author of the study, explains: “Finding methanol in a protoplanetary disc shows the unique capability of ALMA to probe the complex organic ice reservoir in discs and so, for the first time, allows us to look back in time to the origin of chemical complexity in a planet nursery around a young Sun-like star.”
Gaseous methanol in a protoplanetary disc has a unique importance in astrochemistry. While other species detected in space are formed by gas-phase chemistry alone, or by a combination of both gas and solid-phase generation, methanol is a complex organic compound which is formed solely in the ice phase via surface reactions on dust grains.
The sharp vision of ALMA has also allowed astronomers to map the gaseous methanol across the TW Hydrae disc. They discovered a ring-like pattern in addition to significant emission from close to the central star.
The observation of methanol in the gas phase, combined with information about its distribution, implies that methanol formed on the disc’s icy grains, and was subsequently released in gaseous form. This first observation helps to clarify the puzzle of the methanol ice–gas transition, and more generally the chemical processes in astrophysical environments.
Ryan A. Loomis, a co-author of the study, adds: “Methanol in gaseous form in the disc is an unambiguous indicator of rich organic chemical processes at an early stage of star and planet formation. This result has an impact on our understanding of how organic matter accumulates in very young planetary systems.”
This successful first detection of cold gas-phase methanol in a protoplanetary disc means that the production of ice chemistry can now be explored in discs, paving the way to future studies of complex organic chemistry in planetary birthplaces. In the hunt for life-sustaining exoplanets, astronomers now have access to a powerful new tool.
(Image provided with European Southern Observatory news release)
 SpaceX to Launch Inversion RAY Reentry Vehicle in Fall
SpaceX to Launch Inversion RAY Reentry Vehicle in Fall Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.23.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.23.24) Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.20.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.20.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.20.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.20.24) Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.21.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.21.24)



