Planetary Evolution From High Orbit
New gullies that did not exist three years ago have appeared on
a Martian sand dune.

That's just one of the surprising discoveries that have resulted
from the extended life of NASA's Mars Global Surveyor, which this
month began its ninth year in orbit around Mars. Boulders tumbling
down a Martian slope left tracks that weren't there two years ago.
New impact craters formed since the 1970s suggest changes to
age-estimating models. And for three Mars summers in a row,
deposits of frozen carbon dioxide near Mars' south pole have shrunk
from the previous year's size, suggesting a climate change in
progress.
"Our prime mission ended in early 2001, but many of the most
important findings have come since then, and even bigger ones might
lie ahead," said Tom Thorpe, project manager for Mars Global
Surveyor at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. The
orbiter is healthy and may be able to continue studying Mars for
five to 10 more years, he said.
Mars years are nearly twice as long as Earth years. The
orbiter's longevity has enabled monitoring of year-to-year patterns
on Mars, such as seasonal dust storms and changes in the polar
caps. "Mars is an active planet, and over a range of timescales
changes occur, even in the surface," said Dr. Michael Malin of
Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego, principal investigator for
the Mars Orbiter Camera on Mars Global Surveyor.
"To see new gullies and other changes in Mars surface features
on a time span of a few years presents us with a more active,
dynamic planet than many suspected before Mars Global Surveyor got
there," said Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program chief
scientist, NASA Headquarters, Washington.
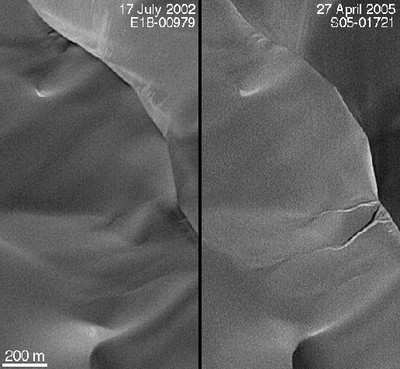
Two gullies appear in an April 2005 image of a sand-dune slope
where they did not exist in July 2002. The Mars Orbiter Camera team
has found many sites on Mars with fresh-looking gullies, and
checked back at more than 100 gullied sites for possible changes
between imaging dates, but this is the first such find. Some
gullies, on slopes of large sand dunes, might have formed when
frozen carbon dioxide, trapped by windblown sand during winter,
vaporized rapidly in spring, releasing gas that made the sand flow
as a gully-carving fluid.
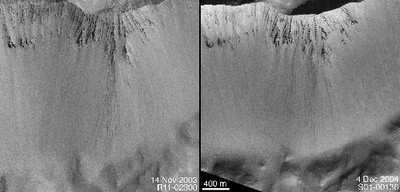
At another site, more than a dozen boulders left tracks when
they rolled down a hill sometime between the taking of images in
November 2003 and December 2004. It is possible that they were set
in motion by strong wind or by a "marsquake," Malin said.
Some changes are slower than expected. Studies suggest new
impact craters might appear at only about one-fifth the pace
assumed previously, Malin said. That pace is important because
crater counts are used to estimate the ages of Mars surfaces.
The camera has recorded seasonal patterns of clouds and dust
within the atmosphere over the entire planet. In addition, other
instruments on Mars Global Surveyor have provided information about
atmospheric changes and year-to-year patterns on Mars as the
mission has persisted. Daily mapping of dust abundance in Mars'
atmosphere by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer has shown dust over
large areas during three Mars southern hemisphere summers in a row.
However, the extent and duration of dust storms varied from year to
year.
Mars Global Surveyor was launched Nov. 7, 1996; entered orbit
around Mars Sept. 12, 1997; and returned the first Mars data from
its science instruments Sept. 15, 1997. Beyond its own
investigations, the orbiter provides support for other Mars
missions, such as landing-site evaluations, atmospheric monitoring,
communication relay and imaging of hardware on the surface. JPL, a
division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena,
manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate,
Washington. JPL's industrial partner is Lockheed Martin Space
Systems, Denver, which built and operates the spacecraft.
 ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.15.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.15.24) Classic Aero-TV: 'No Other Options' -- The Israeli Air Force's Danny Shapira
Classic Aero-TV: 'No Other Options' -- The Israeli Air Force's Danny Shapira Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.15.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.15.24) Airborne 04.16.24: RV Update, Affordable Flying Expo, Diamond Lil
Airborne 04.16.24: RV Update, Affordable Flying Expo, Diamond Lil ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.16.24): Chart Supplement US
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.16.24): Chart Supplement US





