Lost And Found
NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory has discovered two huge
intergalactic clouds of diffuse hot gas. These clouds are the best
evidence yet that a vast cosmic web of hot gas contains the
long-sought missing matter - about half of the atoms and ions in
the Universe.

Various measurements give a good estimate of the mass-density of
the baryons - the neutrons and protons that make up the nuclei of
atoms and ions - in the Universe 10 billion years ago. However,
sometime during the last 10 billion years a large fraction of the
baryons, commonly referred to as "ordinary matter" to distinguish
them from dark matter and dark energy, have gone missing.
"An inventory of all the baryons in stars and gas inside and
outside of galaxies accounts for just over half the baryons that
existed shortly after the Big Bang," explained Fabrizio Nicastro of
the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, and lead author of
a paper in the 3 February 2005 issue of Nature describing the
recent research. "Now we have found the likely hiding place of the
missing baryons."
Nicastro and colleagues did not just stumble upon the missing
baryons - they went looking for them. Computer simulations of the
formation of galaxies and galaxy clusters indicated that the
missing baryons might be contained in an extremely diffuse web-like
system of gas clouds from which galaxies and clusters of galaxies
formed.
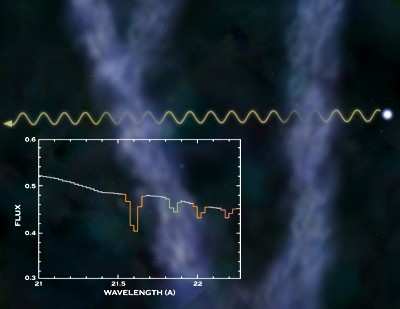
These clouds have defied detection because of their predicted
temperature range of a few hundred thousand to a million degrees
Celsius, and their extremely low density. Evidence for this
warm-hot intergalactic matter (WHIM) had been detected around our
Galaxy, or in the Local Group of galaxies, but the lack of
definitive evidence for WHIM outside our immediate cosmic
neighborhood made any estimates of the universal mass-density of
baryons unreliable.
The discovery of much more distant clouds came when the team
took advantage of the historic X-ray brightening of the quasar-like
galaxy Mkn 421 that began in October of 2002. Two Chandra
observations of Mkn 421 in October 2002 and July 2003, yielded
excellent quality X-ray spectral data. These data showed that two
separate clouds of hot gas at distances from Earth of 150 million
light years and 370 million light years were filtering out, or
absorbing X-rays from Mkn 421.
The X-ray data show that ions of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and
neon are present, and that the temperatures of the clouds are about
1 million degrees Celsius. Combining these data with observations
at ultraviolet wavelengths enabled the team to estimate the
thickness - about 2 million light years - and mass density of the
clouds.
Assuming that the size and distribution of the clouds are
representative, Nicastro and colleagues could make the first
reliable estimate of average mass density of baryons in such clouds
throughout the Universe. They found that it is consistent with the
mass density of the missing baryons.

Mkn 421 was observed three times with Chandra's Low-Energy
Transmission Grating, twice in conjunction with the High Resolution
Camera in May 2000 and July 2003 and once with the Advanced CCD
Imaging Spectrometer in October 2002. The distance to Mkn 421 is
400 million light years.
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., manages
the Chandra program for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington.
Northrop Grumman of Redondo Beach, CA, formerly TRW, Inc., was the
prime development contractor for the observatory. The Smithsonian
Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations
from the Chandra X-ray Center in Cambridge, Mass.
 ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.15.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.15.24) Classic Aero-TV: 'No Other Options' -- The Israeli Air Force's Danny Shapira
Classic Aero-TV: 'No Other Options' -- The Israeli Air Force's Danny Shapira Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.15.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.15.24) Airborne 04.16.24: RV Update, Affordable Flying Expo, Diamond Lil
Airborne 04.16.24: RV Update, Affordable Flying Expo, Diamond Lil ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.16.24): Chart Supplement US
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.16.24): Chart Supplement US





